
Active TB is very serious, causing permanent damage and even death.įor more information, see The Difference Between Latent TB Infection and TB Disease from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A person with active TB has symptoms and can spread TB to others. In active TB (TB disease), TB bacteria become active and multiply. Up to 10% of people with inactive TB who do not receive treatment would develop active TB. TB bacteria can stay alive inside these walls for years. The body builds walls around these bacteria, the way a scab forms over a cut. In inactive (latent) TB, TB bacteria are alive but inactive in the body.

What is the difference between inactive TB and active TB? TB is not as easily transmitted as colds. People who are nearby inhale droplets and may become infected. The bacteria (in the form of droplets) are put into the air when a person with TB coughs or sneezes. TB is spread from person to person through the air. It can also affect other body parts such as the brain, kidneys or spine. Beyond that, health records at UHS are confidential and cannot be released without your consent. UHS must report cases of active TB (but not inactive TB) to the county health department to be investigated for possible contagion of others. TB test results do not affect visa status.
#Arm negative tb test skin#
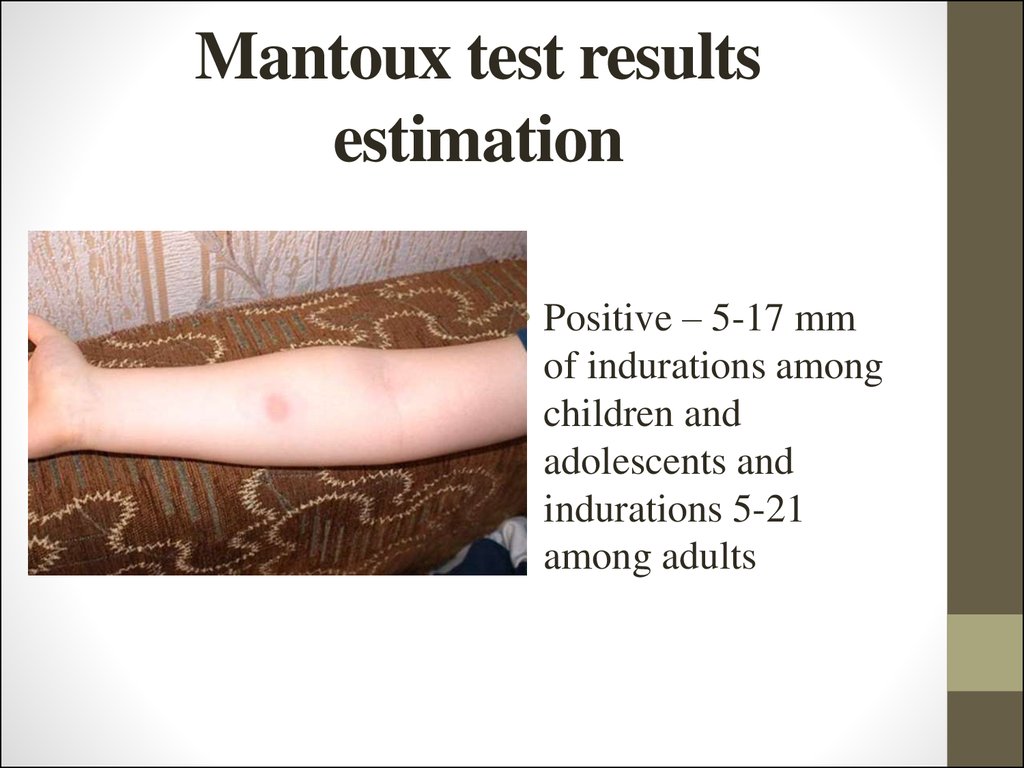
TB infection, not BCG, causes most positive skin tests. Almost all international students who develop active TB have received the vaccine. However, BCG vaccine effectiveness declines with time. Many international patients received BCG vaccine, which reduced their TB risk as children. The BCG TB vaccine generally does not cause a positive skin test result if you were vaccinated more than ten years ago. It is important to keep your record of a positive skin test so you can refer to it in the future and not repeat skin tests.ĭoes vaccination cause a positive skin test? The reaction to a skin test may be stronger if repeated frequently. If I’ve had a positive skin test in the past, should I have another test?Ī blood test may be required after a positive skin test. A positive (reactive) result means there is evidence of TB, additional testing would be required, and you would need to meet with a clinician.A negative (non-reactive) result means no evidence of TB, and no further testing is required.Frequently asked questions about testing: It may cause swelling, itching or tenderness at the site of injection, which usually disappears within a week.īlood testing may be preferred for individuals who received BCG vaccine, had a prior positive TB skin test, or had a documented allergic reaction to the TB skin test in the past. You can do your normal activities after your skin test, including washing your arm. A small amount of fluid (called purified protein derivative or PPD) is injected under the top layer of skin on the lower arm with a small needle. UHS uses the most reliable skin test, the Mantoux PPD. Skin testing is an easy, inexpensive skin test can indicate TB infection, either past or present. If you are a student, bring your U-M ID card with you. You will need to return in person 48-72 hours after the test, so that your arm can be examined to evaluate the results of the test. Skin testing is available at UHS weekdays except Thursday. There are two types of tuberculosis (TB) testing.
#Arm negative tb test how to#
Schedule an appointment by calling 73 or see How to Get Health Care. What is the difference between active TB and inactive TB?.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
